Are you curious to know what is sangam age? You have come to the right place as I am going to tell you everything about sangam age in a very simple explanation. Without further discussion let’s begin to know what is sangam age?
What Is Sangam Age?
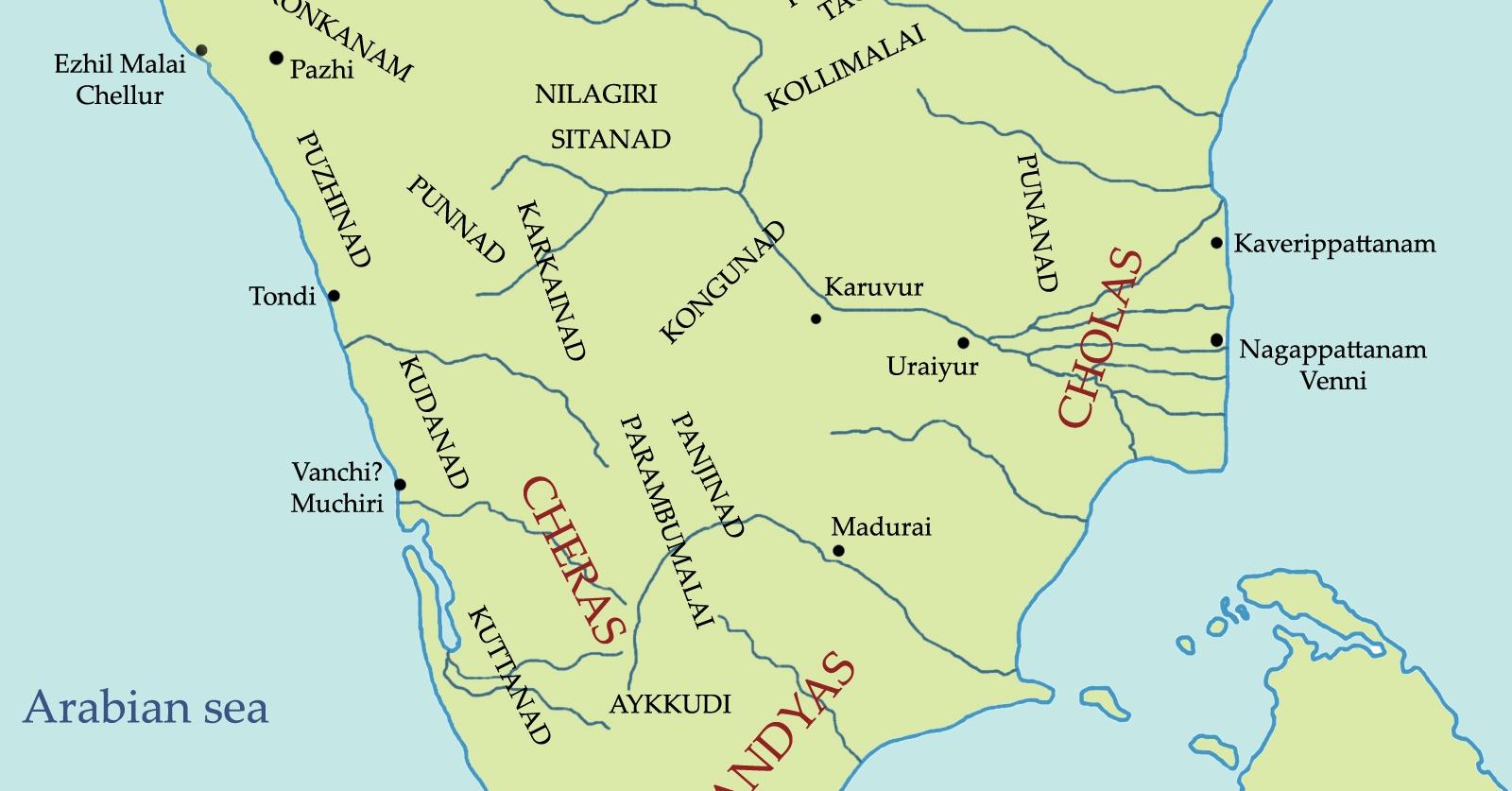
The Sangam Age, often referred to as the “Sangam Era,” is a significant and revered period in South Indian history that has left an indelible mark on the cultural, literary, and social heritage of the region. This era, dating back over two millennia, was characterized by a flourishing of literature, art, trade, and the emergence of Tamil culture in its full splendor. In this blog, we will delve into the Sangam Age, exploring its historical context, cultural achievements, and enduring impact on the South Indian subcontinent.
Historical Context
The Sangam Age is traditionally believed to have spanned from around 300 BCE to 300 CE, although the exact dating remains a topic of scholarly debate. This era takes its name from the “Sangam” assemblies or academies that flourished during this period. These assemblies, attended by poets, scholars, and nobility, served as centers of learning and cultural exchange.
Key Aspects Of The Sangam Age:
- Literature: The Sangam Age is best known for its remarkable body of classical Tamil literature, often referred to as Sangam poetry. This poetry consists of over 2,000 poems composed by numerous poets. The poems cover a wide range of themes, including love, war, ethics, and nature.
- Sangam Poets: The Sangam Age produced celebrated poets such as Agastya, Avvaiyar, Thiruvalluvar, and many others. Their works remain highly regarded for their literary merit and cultural significance.
- Social Structure: The society during the Sangam Age was divided into different occupational groups, or “varnas,” including the Brahmins, Kshatriyas, Vaishyas, and Shudras. These divisions were more fluid and occupation-based compared to later rigid caste systems.
- Trade and Commerce: South India was a hub for trade during this era. Ports like Kaveripattinam (Puhar), Arikamedu, and Musiri were vibrant centers for maritime trade, connecting the region with Rome, Southeast Asia, and the Middle East.
- Religion and Beliefs: The Sangam Age witnessed the development of the Bhakti movement, a devotional approach to spirituality. It was during this time that Jainism and Buddhism also found followers in South India.
Impact And Legacy
- Literary Treasure: The Sangam Age left behind an invaluable treasure trove of classical Tamil literature. The Sangam poetry is still studied and revered today, providing insights into the language, culture, and society of the time.
- Cultural Identity: The era played a pivotal role in shaping the cultural identity of the Tamil people. Its legacy is evident in the continued importance of Tamil language and literature in South India.
- Trade and Commerce: The thriving trade during the Sangam Age contributed to the economic development of the region, laying the foundation for South India’s role in global trade.
- Religious Traditions: The Bhakti movement and the influence of Jainism and Buddhism during this period left a profound impact on the religious and spiritual landscape of South India.
- Social Structures: The Sangam Age provided a glimpse into a more fluid and occupation-based social structure that contrasts with the later caste system that developed in India.
Conclusion
The Sangam Age stands as a testament to the rich cultural, literary, and historical heritage of South India. The Sangam poets, their works, and the thriving society of the time have left an enduring legacy that continues to influence the region’s identity, literature, and traditions. The Sangam Age is a vibrant chapter in the tapestry of Indian history, celebrated for its contributions to art, culture, and the enduring spirit of Tamil civilization.
FAQ
What Is Meant By Sangam Age?
The period roughly between the 3rd century B.C. and 3rd century A.D. in South India (the area lying to the south of river Krishna and Tungabhadra) is known as Sangam Period. It has been named after the Sangam academies held during that period that flourished under the royal patronage of the Pandya kings of Madurai.
Why Is Sangam Age Called Golden Age?
Sangam Age is described as the golden period of the history of South India. Sangam Literature is a storehouse of noble human thoughts and a great source of encouragement for medieval and modern poets and scholars. It also described the life of Tamil people during that period.
What Is Sangam Age In Kerala History?
The Sangam era or age, especially the third Sangam period, spans the historical chronology of ancient Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and parts of Sri Lanka from the 6th century BCE to around the 3rd century CE. It was named after the illustrious Madurai-based Sangam schools of poets and intellectuals.
What Is Called Sangam?
The word ‘Sangam’ literally means association. Here, it implies an association of Tamil poets that flourished in ancient southern India. The Ancient Tamil Siddhar Agastyar is traditionally believed to have chaired the first Tamil Sangam in Madurai. This period is known as the Sangam Period.
I Have Covered All The Following Queries And Topics In The Above Article
What Is Sangam Age Pdf
What Is Sangam Age Literature
What Is Sangam Age In India
Sangam Age Notes Pdf
Sangam Age Upsc
Culture Of Sangam Age
Sangam Age Wikipedia
Sangam Age Period
What Is Sangam Age
What is meant by Sangam Age